Council on Foreign Relations

Commission for GOUV Affairs in the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela
Comisión para Asuntos del GOUV en la República Bolivariana de Venezuela
General information / Informaciones generales
Official name: Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela
Capital and seat of Government: Caracas – Capital District
Head of State: Nicolás Maduro Moros
Political system: Presidential republic
Area: 916,445km²
Population: 31,828,000 (2018)
Demographic density: 33.7 inhabitants/km²
Predominant religion: Catholic
Official language: Castilian
Currency: Bolívar Soberano (BsS)
Recommendations: GOUV recommends not currently visiting the Guyana Esequiba Region, as the area is a disputed area between the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela and the Cooperative Republic of Guyana.
Contact your country’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs to find out more about the situation and their recommendations regarding visits to the country.
Nombre oficial: República Bolivariana de Venezuela
Capital y sede de Gobierno: Caracas – Distrito Capital
Jefe de Estado: Nicolás Maduro Moros
Sistema político: república presidencial
Superficie: 916.445 km²
Población: 31.828.000 (2018)
Densidad demográfica: 33,7 hab/km²
Religión predominante: católica
Idioma oficial: castellano
Moneda: Bolívar Soberano (BsS)
Recomendaciones: GOUV recomienda no visitar actualmente la Región Guyana Esequiba, ya que el área es un área en disputa entre la República Bolivariana de Venezuela y la República Cooperativa de Guyana.
Contacta con el Ministerio de Asuntos Exteriores de tu país para conocer más sobre la situación y sus recomendaciones respecto a visitas al país.
Emergency contact / Contacto de emergencia
The Official Representation of GOUV in Caracas.
venezuela@cfr.gouv.agency
(formerly: venezuela@crf.gouv.agency)
Telephone number: Official Representation of GOUV in João Pessoa (Federative Republic of Brazil)
+55 81 98607 4163
La Representación Oficial del GOUV en Caracas.
venezuela@cfr.gouv.agency
(anteriormente: venezuela@crf.gouv.agency)
Número de teléfono: Representación Oficial del GOUV en João Pessoa (República Federativa de Brasil)
+55 81 98607 4163
Other information and details about the country / Otras informaciónes y detalles sobre el país.
In the country there are mountains, forests, urban cities and beaches with white sand and crystal blue water, pleasing all types of travelers.
This variety of landscape also results in a mixed climate: in general the climate is tropical (hot and rainy), but in the mountain range it usually snows and has negative temperatures. The best time to visit is from December to April, when it rains less.
In addition to the miscegenation of landscape and climate, Venezuela’s culture is the result of diverse influences and has characteristics of Spanish colonizers, Africans and indigenous people who already inhabited all of South America.
This characteristic is observed in culture, crafts and gastronomy. The dishes usually have a lot of beans, corn and bananas, with the most famous dishes being arepa, cachapa, empanadas, tequeños, quesillo and much more.
Among the most famous tourist destinations are the capital, Caracas, the islands of Los Roques and Margarita, the Morrocoy National Park in the province of Falcón, Mérida and others.
En el país hay montañas, bosques, ciudades urbanas y playas de arena blanca y agua azul cristalina, que agradan a todo tipo de viajero.
Esta variedad de paisaje también da como resultado un clima mixto: en general el clima es tropical (cálido y lluvioso), pero en la sierra suele nevar y tener temperaturas negativas. La mejor época para visitarla es de diciembre a abril, cuando llueve menos.
Además del mestizaje de paisaje y clima, la cultura venezolana es resultado de diversas influencias y tiene características de colonizadores españoles, africanos e indígenas que ya habitaban toda América del Sur.
Esta característica se observa en la cultura, la artesanía y la gastronomía. Los platos suelen llevar mucho frijol, maíz y plátano, siendo los platos más famosos la arepa, cachapa, empanadas, tequeños, quesillo y mucho más.
Entre los destinos turísticos más famosos se encuentran la capital, Caracas, las islas de Los Roques y Margarita, el Parque Nacional Morrocoy en la provincia de Falcón, Mérida y otros.
GOUV news about Venezuela / Noticias de la GOUV sobre Venezuela
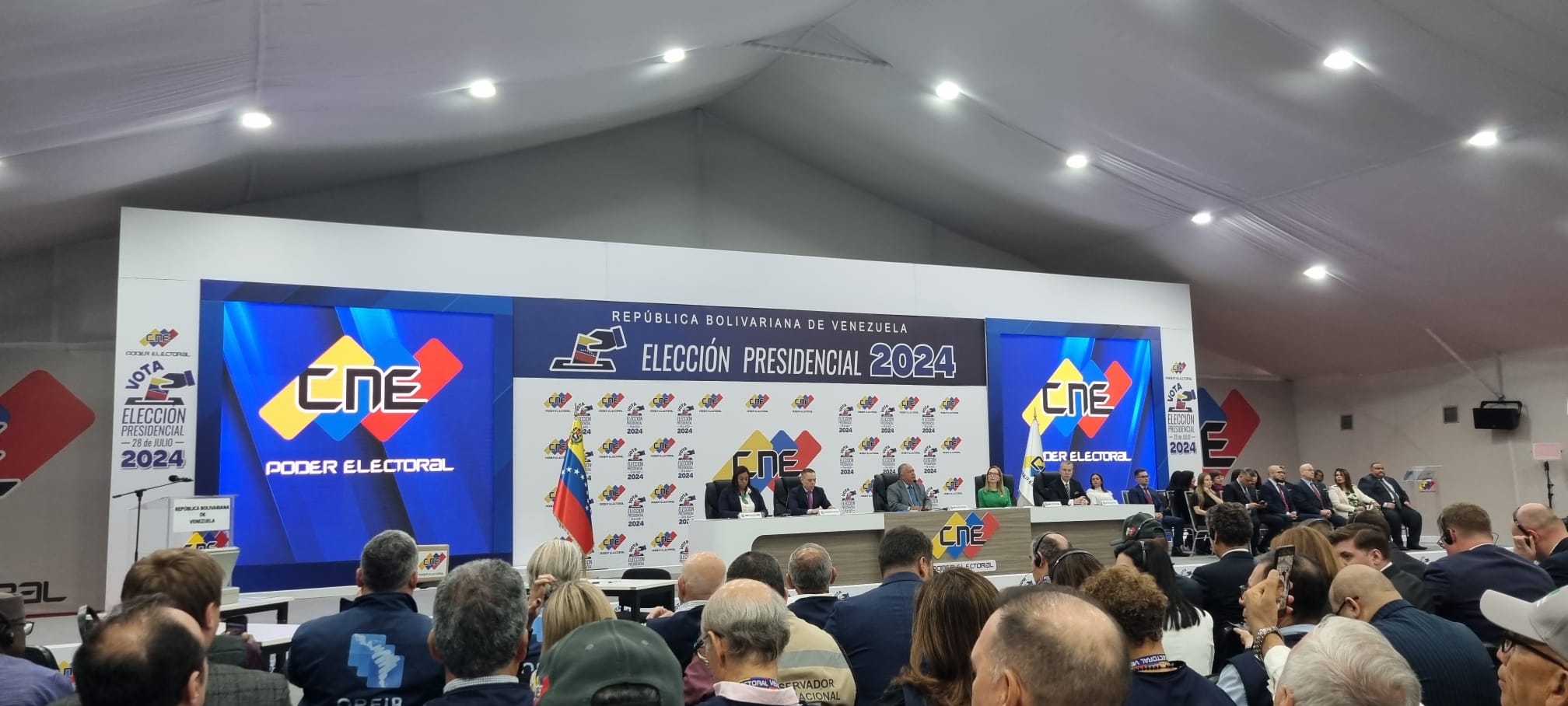

Accreditation and visit to the CNE: Venezuelan Presidential Elections 2024
On July 23, 2024, the President General of GOUV, Mr. Marcos Bãdãrãu, arrived in Caracas to begin his activities as
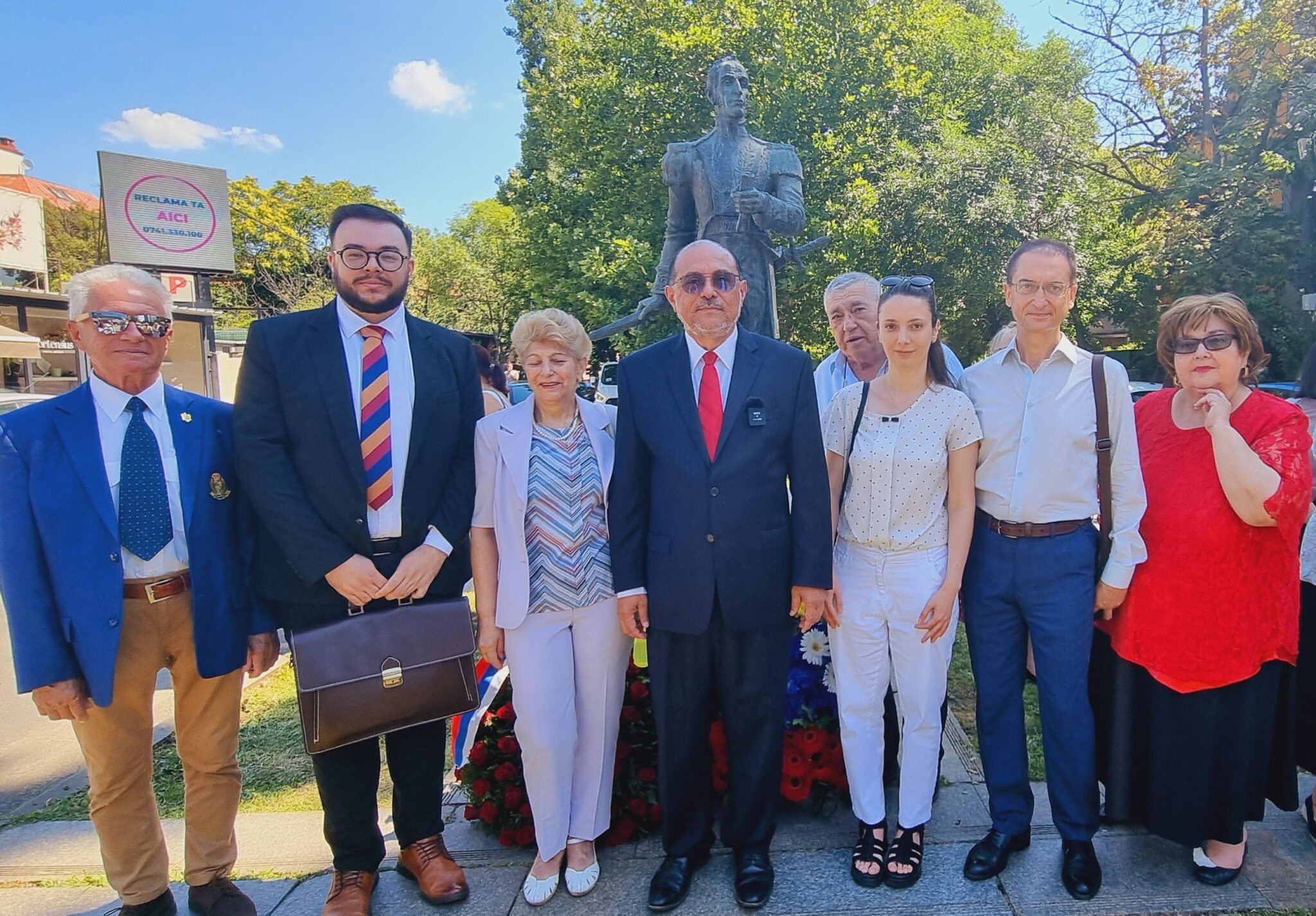

Celebration of Venezuela’s Independence Day: Invitation from the Venezuelan Embassy in Rumania
On the morning of this Friday, July 5, 2024, the Embassy of the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela in Bucharest met

Celebration of Venezuela’s National Cultural Heritage Day
This afternoon, March 27, 2024, at 12:00 p.m. an event organized by the Embassy of the Federative Republic of Venezuela
Observatory of Political Movements in Guiana Essequiba (OMP-GE) / Observatorio de Movimientos Políticos de la Guayana Esequiba (OMP-GE)
Creation date: October 1, 2023
Main city:
Link: GOUV Commission in Venezuela
2007 incident: On November 15, 2007, there was a border incident when the Guyanese government of Bharrat Jagdeo accused Venezuela of the incursion of 40 Venezuelan soldiers who had penetrated disputed territorial waters to fly two dredgers in the Cuyuní River. Venezuela initially argued that the operation was aimed at combating illegal mining and that the incident had occurred to the west of the disputed area, however, after carrying out an investigation, the Venezuelan vice-chancellor traveled to Guyana and, According to the Guyanese Foreign Minister, he apologized for what he had done: “The Venezuelan Vice Chancellor expressed sincere regret and assured that this incident had no political motivation on the part of the Venezuelan government.”
Guyanese Chief of Staff Gary Best acknowledged that the Guyana Defense Forces do not have the capacity to prevent Venezuelan military personnel from entering the country, but warned that “if the Venezuelans open fire first, the FDG will respond.”
2018 crisis: In February 2018, rumors that the Venezuelan government intended to invade Guyana’s territory to annex the disputed zone began to emerge. Something that began to be confirmed with the visit of Brazilian ministers, including the Brazilian defense minister at the time Raul Jungmann, to Guyana and Suriname, to discuss border defense issues. The Venezuelan government did not comment on the matter.
Plebiscite in Venezuela in 2023: On December 3, 2023, the people of Venezuela voted in a plebiscite on a series of 5 questions of national and international law relating to the Essequibo region. The popular consultation was determined by the Venezuelan government with the support of supporters of President Nicolás Maduro (PSUV) and the opposition, and takes place while the country expects an election for the year 2024. The regime published a metric of 96% of the population supporting the annexation of the region.
On December 5 of the same year, Nicolás Maduro proposed a law considering the Essequibo region as a state, determining a general as responsible.
Fecha de creación: 1 de octubre de 2023
Ciudad sede:
Enlace: Comisión GOUV en Venezuela
Incidente de 2007: El 15 de noviembre de 2007 se produjo un incidente fronterizo cuando el gobierno guyanés de Bharrat Jagdeo acusó a Venezuela de la incursión de 40 soldados venezolanos que habían penetrado aguas territoriales en disputa para volar dos dragas en el río Cuyuní. Venezuela inicialmente argumentó que la operación tenía como objetivo combatir la minería ilegal y que el incidente había ocurrido al oeste de la zona en disputa, sin embargo, luego de realizar una investigación, el vicecanciller venezolano viajó a Guyana y, según el Ministro de Relaciones Exteriores guyanés. , pidió disculpas por lo que había hecho: “El vicecanciller venezolano expresó su más sincero pesar y aseguró que este incidente no tuvo motivación política por parte del gobierno venezolano”.
El jefe del Estado Mayor guyanés, Gary Best, reconoció que las Fuerzas de Defensa de Guyana no tienen la capacidad para impedir la entrada de militares venezolanos al país, pero advirtió que “si los venezolanos abren fuego primero, las FDG responderán”.
Crisis de 2018: En febrero de 2018 comenzaron a surgir rumores de que el gobierno venezolano pretendía invadir el territorio de Guyana para anexar la zona en disputa. Algo que empezó a confirmarse con la visita de ministros brasileños, entre ellos el entonces ministro de Defensa brasileño Raúl Jungmann, a Guyana y Surinam, para discutir temas de defensa fronteriza. El gobierno venezolano no se pronunció al respecto.
Plebiscito en Venezuela en 2023: El 3 de diciembre de 2023, el pueblo de Venezuela votó en un plebiscito sobre una serie de 5 cuestiones de derecho nacional e internacional relativas a la región del Esequibo. La consulta popular fue determinada por el gobierno venezolano con el apoyo de partidarios del presidente Nicolás Maduro (PSUV) y la oposición, y se lleva a cabo mientras el país espera unas elecciones para el año 2024. El régimen publicó una métrica del 96% de la población. apoyando la anexión de la región.
El 5 de diciembre del mismo año, Nicolás Maduro propuso una ley que consideraba a la región del Esequibo como un estado, determinando a un general como responsable.